During the summer, you want to be outside all day every day. Whether you’re soaking up the sun at the pool or enjoying a day on the water, you love the feeling of the sun on your skin. You’ve heard people talk about the harmful effects of UV radiation, but you’re not sure what they mean. Here’s what you need to know about UV radiation and how you can use UV protection sunglasses, sunscreen, and other tools to stay safe.

What Is UV Radiation?
UV radiation stands for ultraviolet radiation, which is the kind of radiation that the sun releases. Lasers, fluorescent lights, mercury vapor lights, and tanning beds are other sources of UV radiation. Unlike visible light, which is another type of radiation, you can’t see UV rays. UV radiation is known as a non-ionizing form of radiation because it has lower frequencies than X-rays, Gamma rays, and other kinds of ionizing radiation.
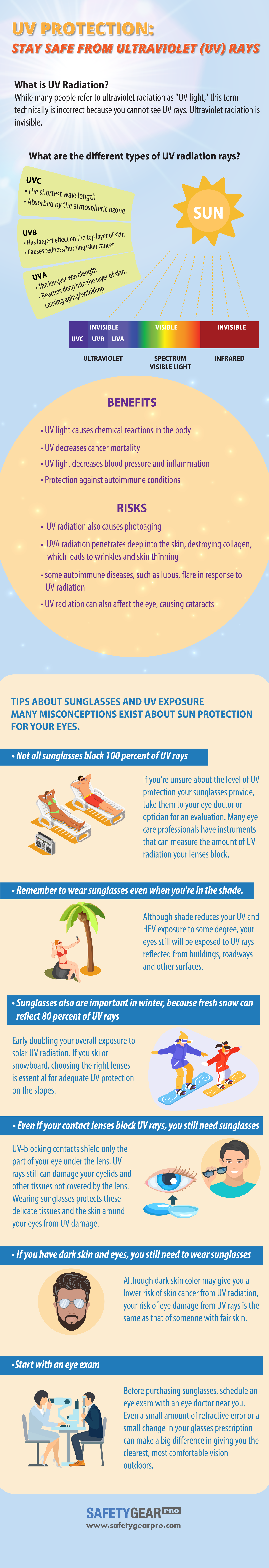
What Are the Different Types of UV Radiation Rays?
There are three main kinds of UV radiation rays, and the one that affects human health the most is Ultraviolet A. The ozone layer does not absorb UVA, so all of the UVA emitted by the sun strikes the Earth. Its wavelengths are between 315 and 399 nanometers long, and while it is weaker than some forms of UV radiation, it is the most common. Also, UVA radiation easily travels into the deepest layers of your skin, causing damage that you can’t easily see.
The next most common form of UV radiation is Ultraviolet B, which the ozone layer largely traps. With wavelengths between 280 and 314 nanometers, UVB is stronger than UVA, but less of it reaches your skin. Also, UVB tends to only affect the parts of your skin that are directly exposed to the sun.
Most people do not talk about the third kind of UV radiation, Ultraviolet C, because the ozone layer stops all of it from reaching the Earth. Its wavelengths are between 100 and 279 nanometers long, making it the most powerful type of UV ray. You don’t need to worry about UVC, though, because you won’t ever be exposed to it unless you leave Earth’s atmosphere.
What Affects UV Exposure?
The level of UV exposure you receive depends on how strong the sun is when you’re outside. When you get closer to the sun, such as when you’re close to the equator or at a high altitude, you receive more UV rays. Also, because the sun is closer to the Earth during spring and summer, UV rays are stronger then. When you’re around a lot of shiny surfaces, such as cars or bodies of water, the opportunities for reflection amplify any UV radiation you’re exposed to.
If you’re ever unsure about the level of UV radiation in your area, check out the UV Index, which the Environmental Protection Agency and the National Weather Service run. The index starts at one, for a low amount of UV radiation, and ends at 11, for a high amount of radiation. Checking the index helps you determine if UV protection sunglasses offer enough protection or if you need sunscreen, too.
Benefits of UV Radiation
Many people focus on UV radiation’s risks, but it also has some benefits. Exposure to the sun gives you access to vitamin D, which helps you absorb calcium and boosts your immune system. When you’re low on vitamin D, it’s easy to develop osteoporosis or rickets. While scientists aren’t sure how much vitamin D you need every day, you can get enough to keep you healthy from the sun.
Risks of UV Radiation
Despite the Vitamin D-related benefits of UV radiation, overexposure to UV rays can cause many diseases. Skin cancer, eye cancer, cataracts, and other diseases result from UV ray damage. Also, if your eyes are exposed to too much UV radiation, you can get headaches and eye fatigue.
Protect Yourself From UV Radiation
Thankfully, there are many ways to protect yourself from UV radiation. Avoid tanning beds and sun lamps, because these artificial light sources produce excessive amounts of UV radiation. Whenever you go outside, apply sunscreen that has a sun protection factor of at least 15 or higher, and reapply the lotion every two hours. Remember that sunscreen wears off more quickly if you’re sweating a lot or swimming, so you may need to reapply it more frequently.
Don’t forget to put on a pair of sunglasses to protect your eyes from UV radiation whenever you’re driving or hanging out outside. The best sunglasses for UV protection come with UV protection such as polarization, which keeps your eyes safe from glare.
Frequently Asked Questions About UV Radiation
1. Do UV Protection Sunglasses Work?
UV protection sunglasses block UV rays and reflect them back into your surroundings. If they’re rated for UV protection or labeled as polarized, they should keep your eyes safe. Make sure that they’re not just intended to be fashion accessories, though. Only purchase sunglasses that are guaranteed to protect your eyes.
2. What if You Are Allergic to Sunscreen?
If you develop a rash when you’re wearing sunscreen, you’re probably allergic to oxybenzone, which keeps out the sun’s rays, or the perfumes that are mixed in. Once you’ve treated your rash with topical lotion or antihistamines, try sunscreens that list titanium dioxide or zinc oxide as their active ingredient.
3. What if It's Cloudy Outside?
Clouds limit the amount of UV radiation that passes from the sun to your skin. However, they don’t completely block UVA and UVB, so while you can take off your sunglasses to help you see, you should still wear sunscreen. You don’t know when the sun will return at full strength, so play things safe by wearing sunscreen.
4. What Times of Day Pose the Greatest Risk?
The sun tends to be the strongest between 10 in the morning and four in the afternoon. If you’re outside during these times, make sure to apply sunscreen, wear protective shirts and hats, and put on your sunscreen. In the early morning and late afternoon, your eyes still need your sunglasses’ protection, but you can probably skip the sunscreen.
5. What Are Other Sources of Vitamin D?
UV radiation isn’t the only source of vitamin D, so if you have sensitive skin, don’t worry. Egg yolks, red meat, and many kinds of fish are full of vitamin D, and lots of cereals are fortified with it. If you have a serious deficiency, ask your doctor about vitamin D pills or syrups. To receive the benefits of UV radiation while keeping your eyes safe from its harmful effects, choose a pair of UV protection glasses from Safety Gear Pro today.

Top 5 Polarized Sunglasses for Men
1. Oakley Radar
Oakley’s Radar sport sunglasses are the perfect choice for the cyclist or sports participant. Because they wrap around the face, they offer great peripheral vision protection as well. You might have seen a baseball player or two sporting these great frames.
2. Oakley Holbrook
For more casual settings, the Oakley Holbrook is fashioned for classic style and comfort. Whether you prefer plastic or metal is not a problem, because the Holbrook comes in either.
3. Costa Rincon
The Costa Rincon has a large lens design, making them the perfect choice for fishermen. They offer comfort with spring hinges, and they can be customized to include your prescription. You have the choice of plastic or glass for your lenses.
4. Costa Fantail
Also great for fisherman, but with a smaller lens and frame.
5. Oakley Sutro
The Oakley Sutro was designed with cyclists in mind. The large lenses offer protection as well as polarized protection for those days when all you want to do is ride.